Together, we can create a world ready to face any storm, snow, or sunshine!
Weather can be unpredictable, but preparation can make all the difference between chaos and calm. One recent example of extreme weather management in action is the Lake Effect Snow Emergency in the United States, which has captured global attention due to its sheer intensity and the coordinated response by local governments. But why discuss this topic today, and what relevance does it hold for Indian cities? Let’s break it down, word by word, to understand the significance.
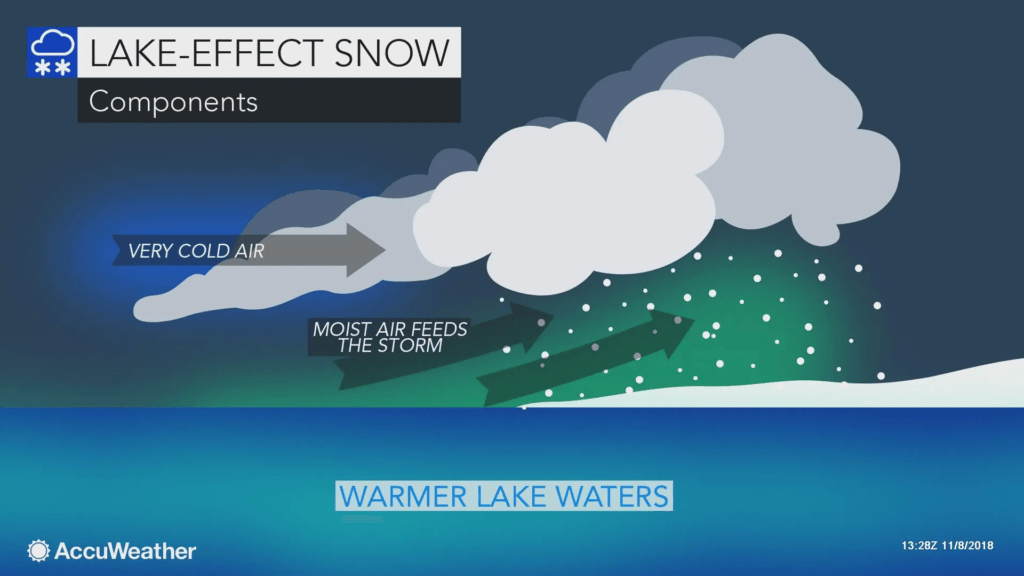
- Lake Effect Snow: A natural phenomenon resulting from cold air passing over warmer lake waters, producing intense, localized snowstorms. While it’s a feature of winters in regions around the Great Lakes in the U.S., its effects ripple beyond borders as an example of managing extreme weather.
- Emergency: The term underscores the urgency and preparedness required to address not just snow but any severe weather event. Emergencies call for decisive action, a robust response system, and public cooperation—lessons that can resonate worldwide.
- U.S.: Known for its advanced disaster management systems, the United States has long been a global reference point for emergency preparedness. The recent actions by Governor Kathy Hochul during a severe snowstorm in New York highlight best practices that Indian cities can adapt to their unique challenges.
- What Can Indian Cities Learn: Here lies the core of the discussion. As climate change intensifies, Indian cities face their own weather emergencies—heatwaves, cyclones, floods, and more. Learning from global examples like Lake Effect Snow management can be a valuable step in enhancing local resilience.
- About Weather Readiness: This isn’t just about reacting to disasters but being proactive—investing in infrastructure, education, and technology to minimize the impact of extreme weather.
Let’s dive deeper into the Lake Effect Snow Emergency in the U.S., understand its mechanics, and explore actionable takeaways for Indian cities.
What is Lake Effect Snow?
Lake Effect Snow occurs when cold, dry air moves over large, warm lake surfaces. The interaction causes the air to absorb moisture and heat, which rises and cools as it moves away from the lake. The result? Heavy, localized snowfall often accompanied by strong winds.
- Magnitude: In some cases, Lake Effect Snow can deposit up to 2 to 5 inches of snow per hour, creating whiteout conditions and making travel nearly impossible.
- Regions Affected: The phenomenon is most common around the Great Lakes region, including parts of New York, Pennsylvania, and Ohio.
This meteorological marvel, while fascinating, is also a reminder of nature’s power, demanding immediate and organized responses.
When Do Lake Effect Snow Emergencies Typically Occur?
Lake Effect Snow is a winter phenomenon, usually occurring between November and February, when:
- Lake Temperatures Are Warmer: Autumn heat retained in the water contrasts sharply with cooler air temperatures.
- Cold Air Masses Move In: Arctic air sweeps in, triggering snowstorms.
- Wind Direction Aligns: Specific wind patterns determine which areas receive the most snow.
Recent emergencies, like the November 2022 snowstorm in Buffalo, New York, showcased the critical need for readiness during these peak months.
Where Are Lake Effect Snow Emergencies Most Common?
The Great Lakes region in the northeastern U.S. is synonymous with Lake Effect Snow. Areas frequently impacted include:
- Buffalo, New York: A city known for its proximity to Lake Erie and its history of heavy snowfalls.
- Syracuse, New York: Regularly ranked among the snowiest cities in the U.S.
- Cleveland, Ohio: Another hotspot for extreme snowfall.
These locations experience some of the highest snowfall totals annually due to their geographic placement and climate conditions.
Who Manages a Lake Effect Snow Emergency?
Managing a Lake Effect Snow Emergency requires collaboration between various entities:
- State Governments: Leaders like Governor Kathy Hochul take the lead in declaring emergencies and allocating resources.
- Local Authorities: City and county governments manage road clearing, shelters, and public safety.
- Federal Agencies: Organizations like FEMA (Federal Emergency Management Agency) provide additional support during extreme events.
- Community Members: Residents play a role by heeding warnings, following guidelines, and helping neighbors.
The multi-layered approach ensures that resources are efficiently deployed, minimizing the loss of life and property.
Why Are Lake Effect Snow Emergencies Significant?
The significance of these emergencies lies in their impact:
- Economic Disruption: Heavy snowstorms can halt businesses, delay logistics, and cause millions in damages.
- Public Safety Concerns: Power outages, road accidents, and hypothermia are just a few risks posed by extreme cold.
- Infrastructure Challenges: Clearing roads and restoring services in heavy snow conditions is both time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Climate Change Implications: While snowstorms may seem like cold-weather events, they are intricately linked to climate patterns that affect global weather systems.
Indian cities, though not affected by snow, face comparable challenges with floods, heatwaves, and cyclones, making these lessons universally applicable.
How Does the U.S. Handle Such Emergencies?
The U.S. response to Lake Effect Snow emergencies involves meticulous planning and execution:
- Advanced Weather Forecasting: Agencies like the National Weather Service (NWS) issue early warnings, giving residents time to prepare.
- Emergency Declarations: Governors can activate resources, such as the National Guard, to assist in snow removal and rescue operations.
- Public Communication: Real-time updates through social media, television, and mobile alerts ensure widespread awareness.
- Infrastructure Investment: Snowplows, salt stockpiles, and heated roads are part of the preparation to mitigate snow-related disruptions.
- Community Outreach: Efforts to educate citizens on snow safety, including proper insulation and emergency kits, are widespread.
Whose Responsibility Is Weather Readiness in India?
India’s unique climate demands localized solutions for weather emergencies. Here’s a breakdown of responsibility:
- Government Agencies: The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) oversees disaster preparedness, while local governments implement strategies.
- Private Sector: Companies can contribute by investing in resilient infrastructure and employee safety measures.
- Non-Governmental Organizations: NGOs play a crucial role in educating communities and providing aid during disasters.
- Citizens: Individual preparedness, like stocking essentials and adhering to guidelines, is equally important.
Lessons Indian Cities Can Learn from Lake Effect Snow Emergencies
- Early Warning Systems: Investing in technology to predict weather events can save lives and resources.
- Example: Odisha’s cyclone warning system is a model for disaster preparedness in India.
- Clear Communication: Transparent, real-time updates can reduce panic and ensure public cooperation.
- Fact: Over 70% of Indian states lack adequate communication infrastructure during disasters.
- Infrastructure Resilience: Building flood-resistant roads or heatwave shelters can mitigate the impact of extreme weather.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in preparedness plans ensures better implementation.
- Climate Adaptation Policies: Addressing the root causes of extreme weather through sustainable practices is essential.
Final Thoughts: A Call for Global Weather Readiness
The Lake Effect Snow Emergency in the U.S. is more than just a regional phenomenon—it’s a blueprint for managing extreme weather worldwide. For Indian cities grappling with their own challenges, the lessons in preparedness, collaboration, and resilience are invaluable.
By learning from these global examples, India can enhance its ability to respond to disasters, protect its citizens, and build a future where weather emergencies are met with confidence rather than chaos.
The question isn’t just about what we can learn—it’s about how quickly we can act on those lessons.

